
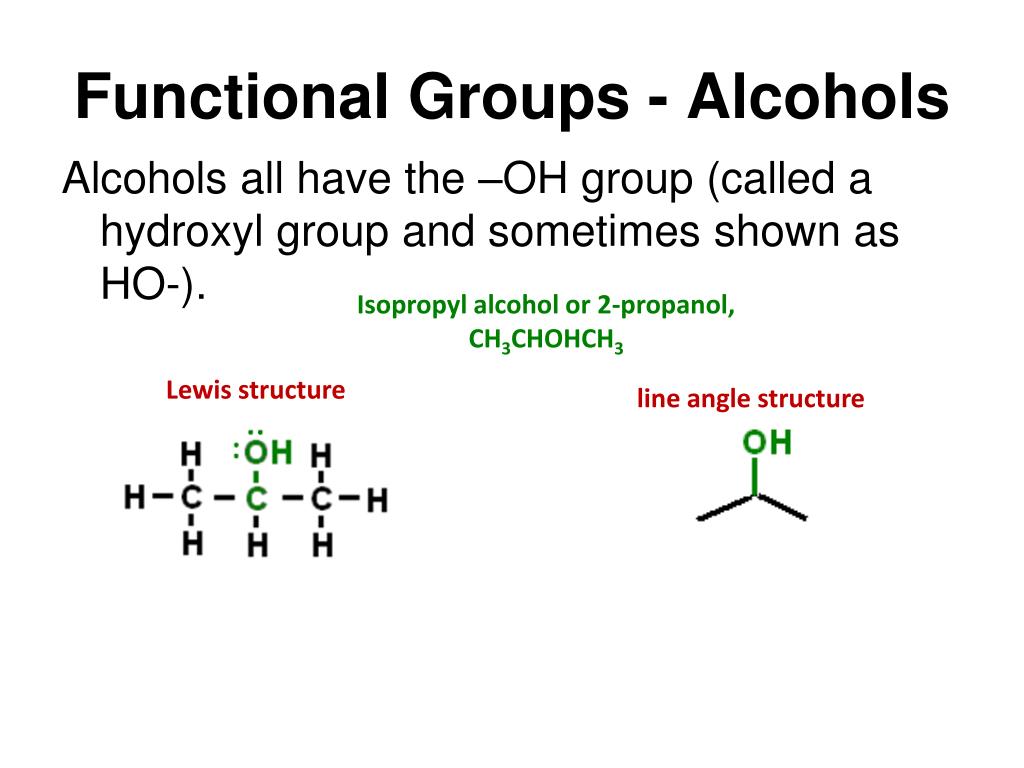
Gives higher yields and cleaner product mixtures because rearrangements are The advantage is that the mercuric electrophileįorms a bridged or partially bridged intermediate that is stabilized and hence Serves as a surrogate for the proton during the addition step and is replacedīy hydrogen in the reduction. Reductive removal of mercury with NaBH 4. For example, the preferred way to produce the Markovnikov alcoholįrom an olefin is to use hydroxymercuration for the addition step followed by Instead methods are used which permit much greater regiochemical control andĪre milder. However, simpleĪcid-catalyzed addition of water is often the least desirable alternative. Thus a common method for the preparation of alcohols. Addition of water across an olefinic dou-ble bond is Aldehydes give primary alcohols while ketonesĪnd olefins are at the same oxidation level and are interconvertible without aĬhange in oxidation level. Milder than LAH and does not require aprotic conditions (an alcohol is often As such it provides a selective way to reduce acidsĪnd produce alcohols in the presence of most other functional groups.Īnd ketones are conveniently reduced by sodium borohydride, which is much Increases the reactivity of the boron hydride and delivers the hydride by an Unique reactivity comes from the fact that borane first forms a Lewis acid –īase complex with the acid and then a boron – carboxylate intermediate which With carboxylic acids than with esters or other acid derivatives. Reduced easily by borane, which is the only reducing agent that reacts faster Carboxylic acids, but not esters, are also Reductive methods have been reported for the preparation of alcohols.Ĭarboxylic acids and esters react vigorously with lithium aluminum hydride Groups and consequently are readily prepared by reduction. Methods for the preparation of alcohols are still among the most usefulĪre at a fairly low oxidation level compared to other oxygen-containing functional The alcohol group, but the alcohol group can be prepared from many other groups and converted to many functional groups. Not only do many important compounds and pharmaceuticals contain Not only do many important compounds and pharmaceuticals contain the alcohol group, but the alcohol group can be prepared from many other groups and converted to many functional groups.Īlcohol functional group is a very important functional group in organicĬhemistry. The alcohol functional group is a very important functional group in organic chemistry.
Naming phenols can be done in many ways.Ĭontinue reading about the other functional groups.Chapter: Organic Chemistry : Functional Group Synthesis When the hydroxyl group is bonded directly to a benzene ring, the compound is classified as a phenol. If it is bonded to three other carbons, it is a tertiary (3 o) alcohol. If this carbon is bonded to two other carbons, it is a secondary (2 o) alcohol. If this carbon is bonded to one other carbon atom, it is a primary (1 o) alcohol. Just as with alkenes, alkynes, and ketones, the location of the hydroxyl group is made by numbering the molecule such that the hydroxyl group has the lowest number possible.Īlcohols are subdivided by examining the carbon to which the hydroxyl group is bonded. Structure Example Compound Official Name of ExampleĪ hydroxyl group is a hydrogen bonded to an oxygen that is covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
